Sharing a few simple tips on data wrangling using Python Pandas library! Does having to clean messy excel datasets sound familiar to you? This post explains on 1) how to convert dataframes from wide to long format, 2) standardising column names and 3) dividing column values evenly across duplicated Indexes.
- Step 1: Import the Pandas libraries
- Step 2: Import excel and read as dataframe ‘df’
- Step 3: Convert df from wide to long format (gather columns into rows)
- Step 4: Standardise the column names
- Step 5: Create a new ID column by concatenating
Project Name,Project I/DandG/L Account - Step 6: Split “gl_account” column, expand it, stack it, then join back to the original mdf
- Step 7: Parse values in str to int
- Step 8: Divide monthly budget value evenly across duplicated indexes
- Step 9: Drop the concatenated unqiue ID column
proj_gl_idas it is not required.
Step 1: Import the Pandas libraries
import pandas as pd
Step 2: Import excel and read as dataframe ‘df’
df = pd.read_excel('yourexcelfile.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
Let’s take the dataframe of your monthly budget excel sheet (in wide format) to be the following:
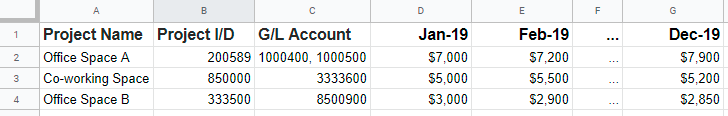
Step 3: Convert df from wide to long format (gather columns into rows)
We will use pd.melt to gather columns into rows. First, identify all the columns which you want to retain (no changes made), these will be labelled as id_vars. Next, identify the column which you want to convert from columns to rows format, this will be labelled as var_name.
Then, assign a name to the value of your converted column as value_name.
mdf = pd.melt (df, id_vars=["Project Name", "Project I/D", "G/L Account"],
var_name="Period", value_name= "Monthly Budget")
Step 4: Standardise the column names
Let’s standardise the column names with lower case and replacing all special characters (‘’ spaces and /) in mdf column names with _ (underscores).
mdf.columns = mdf.columns.str.strip().str.lower().str.replace(' ','_').str.replace('/','')
print(mdf.columns)
Step 5: Create a new ID column by concatenating Project Name, Project I/D and G/L Account
For indexing purpose, let’s create a new unique identifier column and store the new ID column as proj_gl_id.
mdf['proj_gl_id'] = mdf['project_name'].map(str) +'-'+ mdf['project_id'].map(str) + '-' + mdf['gl_account'].map(str)
Step 6: Split “gl_account” column, expand it, stack it, then join back to the original mdf
As there are two GL line items for the same Project in the 1st row of data, we need to first split the str by ‘,’ in the gl_account column, then stack the expanded gl_account columns into 2 rows.
sdf = mdf.drop('gl_account', axis=1).join(mdf['gl_account'].str.split(', ', expand=True).stack().reset_index(level=1, drop=True).rename('gl_account'))
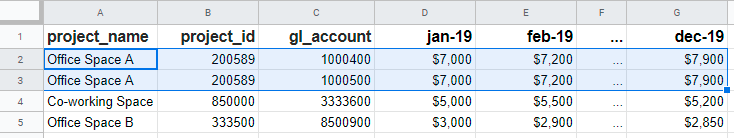
Now, we have 2 duplicated budget GL line items (as highlighted) with budget value at twice the amount of its original value.
Step 7: Parse values in str to int
The current dataframe stores the values in str format. To do any calculation, we need to convert the values to int.
sdf['monthly_budget'] = pd.to_numeric(sdf['monthly_budget'], errors ='coerce')
Step 8: Divide monthly budget value evenly across duplicated indexes
To get the individual budget amount for each GL line item, we will need to divide the budget value amount evenly across the duplicated indexes.
sdf['budget'] = sdf.groupby([sdf.index])['monthly_budget'].apply(lambda x: x / len(x))
Step 9: Drop the concatenated unqiue ID column proj_gl_id as it is not required.
Store the updated dataset as res. Export res to csv, removing the index column.
res = sdf.drop('proj_gl_id',axis =1)
res.to_csv('Budget_2019.csv',index = False)
There you go, a clean dataframe in long format!
Full python code here:
import pandas as pd
# read excel file
df = pd.read_excel('yourexcelfile.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
# convert from wide to long format
mdf = pd.melt (df, id_vars=["Project Name", "Project I/D", "G/L Account"],
var_name="Period", value_name= "Monthly Budget")
# standardise column names
mdf.columns = mdf.columns.str.strip().str.lower().str.replace(' ','_').str.replace('/','')
print(mdf.columns)
# create unique ID
mdf['proj_gl_id'] = mdf['project_name'].map(str) +'-'+ mdf['project_id'].map(str) + '-' + mdf['gl_account'].map(str)
# split text in column
sdf = mdf.drop('gl_account', axis=1).join(mdf['gl_account'].str.split(', ', expand=True).stack().reset_index(level=1, drop=True).rename('gl_account'))
# convert text str to numeric
sdf['monthly_budget'] = pd.to_numeric(sdf['monthly_budget'], errors ='coerce')
# divide values evenly across duplicated indexes
sdf['budget'] = sdf.groupby([sdf.index])['monthly_budget'].apply(lambda x: x / len(x))
# retrieve your desired dataset
res = sdf.drop('proj_gl_id',axis =1)
res.to_csv('Budget_2019.csv',index = False)
