Sharing and documenting the basic concepts of batch scripting which I’ve picked up at work. Hopefully this blog post entry can help you to learn the basics of batch scripting and create scripts to automate tasks which are repetitive in nature.
- What is a batch script?
- How to create a batch file in windows?
- Where am I? What’s in this directory?
- Commands: SET, ECHO, MOVE
What is a batch script?
A batch script is a text file that contains certain commands that are executed in sequence, one after the other. Some of the common uses of batch script are:
- Automating housekeeping activities such as deleting unwanted files or log files.
- Automating the deployment of applications from one environment to another.
- Installing programs on various machines at once.
- Setting up servers for different purposes.
- Backing up folder/filesystem to another location
A batch script has a file extension of .bat, .cmd or .btm. Files of this type are recognized and executed through an interface (sometimes called a shell) provided by a system file called the command interpreter. On Windows systems, this interpreter is known as cmd.exe.
How to create a batch file in windows?
- Open a text file, such as a Notepad or WordPad document.
- Add your commands, starting with
@echo [off], followed by—each in a new line—title [title of your batch script],echo [first line], andpause. - Save your file with the file extension
.bat, for example, test.bat. - To run your batch file, double click the BAT file you just created.
- To edit your batch file, right-click the BAT file and select Edit.
Some general rules to keep in mind when naming batch files −
- Try to avoid spaces when naming batch files, it sometime creates issues when they are called from other scripts.
- Don’t name them after common batch files which are available in the system such as ping.cmd.
Where am I? What’s in this directory?
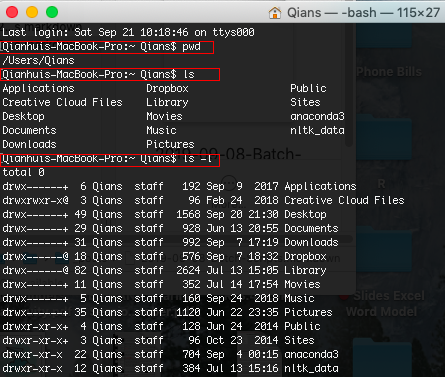
pwd
stands for Print Working Directory. It prints the path of the working directory, starting from the root.
ls
list all files and directories in your current directory
ls -l
list out all files and directories in long list format
The output in git bash will look like this:
Commands: SET, ECHO, MOVE
SET
We use the SET command to create a new named variable and set its value. We can also use the SET /A command if we want to perform arithmetic on a variable.
- Variables: SET variable = value
- Arithmetic: SET /A variable = expression
(e.g. SET /A "_number= _number+5")
ECHO
This batch command displays messages, or turns command echoing on or off. @echo offensures that our commands are executed instead of being echo-ed back in the command window as messages.
Syntax
ECHO string or
ECHO %variable%
Below shows an example of the script written in the .bat file. `Rem` is the remarks function.
Rem Turns the echo on so that each command will be shown as executed
echo on
echo "Hello World"
Rem Turns the echo off so that each command will not be shown when executed
@echo off
echo "Hello World"
Rem Displays the contents of the PATH variable
echo %PATH%
The following output will be displayed in the command prompt:
C:\>Rem Turns the echo on so that each command will be shown as executed
C:\>echo on
C:\>echo "Hello World"
"Hello World"
C:\>Rem Turns the echo off so that each command will not be shown when executed
"Hello World"
C:\Users\ADMIN\AppData\Local\Temp
MOVE
This batch command moves files or directories between directories.
Syntax
move [source] [destination]
The following example shows the different variants of the move command.
@echo off
Rem Moves all .csv files name starting with "august" august%.csv to the directory c:\tp
move C:\august%.csv c:\tp
Rem Renames directory Dir1 to Dir2, assuming Dir1 is a directory and Dir2 does not exist.
move Dir1 Dir2
Rem Moves the file lists.txt to the current directory.
move C:\lists.txt
Output:
All actions are performed as per the remarks in the batch file.
Using commands of SET, ECHO, MOVE altogether:
- Create the source and destination directory variable using
SETcommand. - Display how the files will be moved using the
ECHOcommand. - Move the files using the
MOVEcommand.
@ECHO OFF
SETLOCAL ENABLEDELAYEDEXPANSION
SET "sourcedir=C:\Users\desktop"
SET "destdir=C:\Users\documents"
ECHO MOVE "%sourcedir%\august%.csv" "%destdir%"
MOVE "%sourcedir%\august%.csv" "%destdir%"
